+90 533 813 89 77
info@bookingforhealth.com
Reproductive Health
Reproductive health refers to the complete physical, mental, and social well-being related to fertility. It encompasses a wide range of issues, including access to sexual and reproductive health services, contraception and family planning, maternal health, and gender-based violence.
Reproductive health is important for a number of reasons. It allows people to make informed decisions about their sexual and reproductive lives, and to have access to the resources and services they need to do so.
It also plays a key role in reducing maternal and infant mortality rates, and can help prevent the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
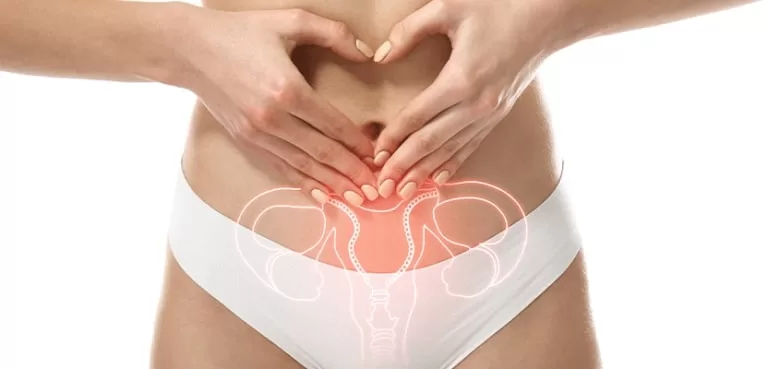
What is Fertility?
Fertility is the ability to conceive and give birth to a child. It is an important aspect of reproductive health for individuals and couples who wish to start or expand their families.
It can be affected by a variety of factors, including genetics, age, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions. Understanding fertility and the factors that can impact it is essential for individuals and couples who are trying to conceive, as well as for those who may be considering assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
With the right knowledge and support, many people are able to overcome fertility challenges and achieve their dream of starting a family.

Common Reproductive Health Concerns
There are many common reproductive health concerns, including infertility, unplanned pregnancies, and STIs. Infertility affects both men and women and can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, genetics, and lifestyle choices.
Unplanned pregnancies can also have a significant impact on an person’s life and can lead to a number of health and social issues. STIs, including HIV, can also have serious consequences if left untreated.
How to Maintain and Improve Reproductive Health?
There are a number of things that individuals can do to maintain and improve their reproductive health. These include:
- Practicing safe sex to prevent STIs and unplanned pregnancies
- Regularly visiting a healthcare provider for check-ups and screenings
- Using contraception to prevent pregnancy
- Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and not smoking or using drugs
- Being informed about different reproductive health issues and services
What is Maternal Health?
Maternal health refers to the health of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. It involves a wide range of issues, including access to prenatal and nativity care, nutrition, and support for mental and emotional well-being. Ensuring good maternal health is essential for the health of both mother and baby.
During pregnancy, regular prenatal care is important to monitor the health of the mother and the baby. This includes regular check-ups, screenings, and testing for any potential complications. Proper nutrition is also crucial for maternal health and the development of the baby.
Childbirth care is also a vital aspect of maternal health, as it can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of both mother and baby. This includes access to safe and skilled birth attendants, as well as access to emergency obstetric care in case of complications.
After giving birth, postpartum care is important for the mother’s physical and emotional recovery. This includes check-ups, support for breastfeeding, and resources for mental and sensual well-being.
Maternal health is an important issue globally, particularly in low-income countries where maternal mortality rates are high. Many of these deaths are preventable with access to proper healthcare, education, and support.
Ensuring good maternal health is essential for the health of both mother and baby and it is the responsibility of the government, healthcare providers and society to ensure that women have access to the care they need to have a safe pregnancy, birth and postpartum recovery.
Birth Control Methods
Contraception, also known as birth control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent pregnancy. There are several different types of it available, each with their own unique benefits and drawbacks.
- Hormonal Contraception: This includes practices such as the birth control pill, the patch, the ring, injections, and the implant. These methods use hormones to prevent ovulation, and they are highly effective when used correctly.
- Barrier Methods: Such as condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps. These methods physically block the sperm from reaching the egg, and they also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Long-acting Reversible Contraception (LARC): These ways such as IUDs (intrauterine devices) and the implant, are long-term, highly effective, and reversible.
- Fertility Awareness Methods (FAMs): These include natural family planning, the rhythm practice, and the basal body temperature method, which involve monitoring a woman’s menstrual cycle to determine when she is most fertile.
- Sterilization: It involves permanent methods such as tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men.
It is important to note that no method of contraception is 100% effective, and the best method for an individual will depend on factors such as overall health, personal preferences, and the person’s lifestyle.
It is also ivital to have a conversation with a doctor to determine the best method, as well as to discuss potential side effects and any other concerns. If you have any questions about reproductive health or want to get more detailed information about these issues, make a consultation with Booking for Health right away. Please contact us.